Randomized Padding
📦 Why Padding Is Needed
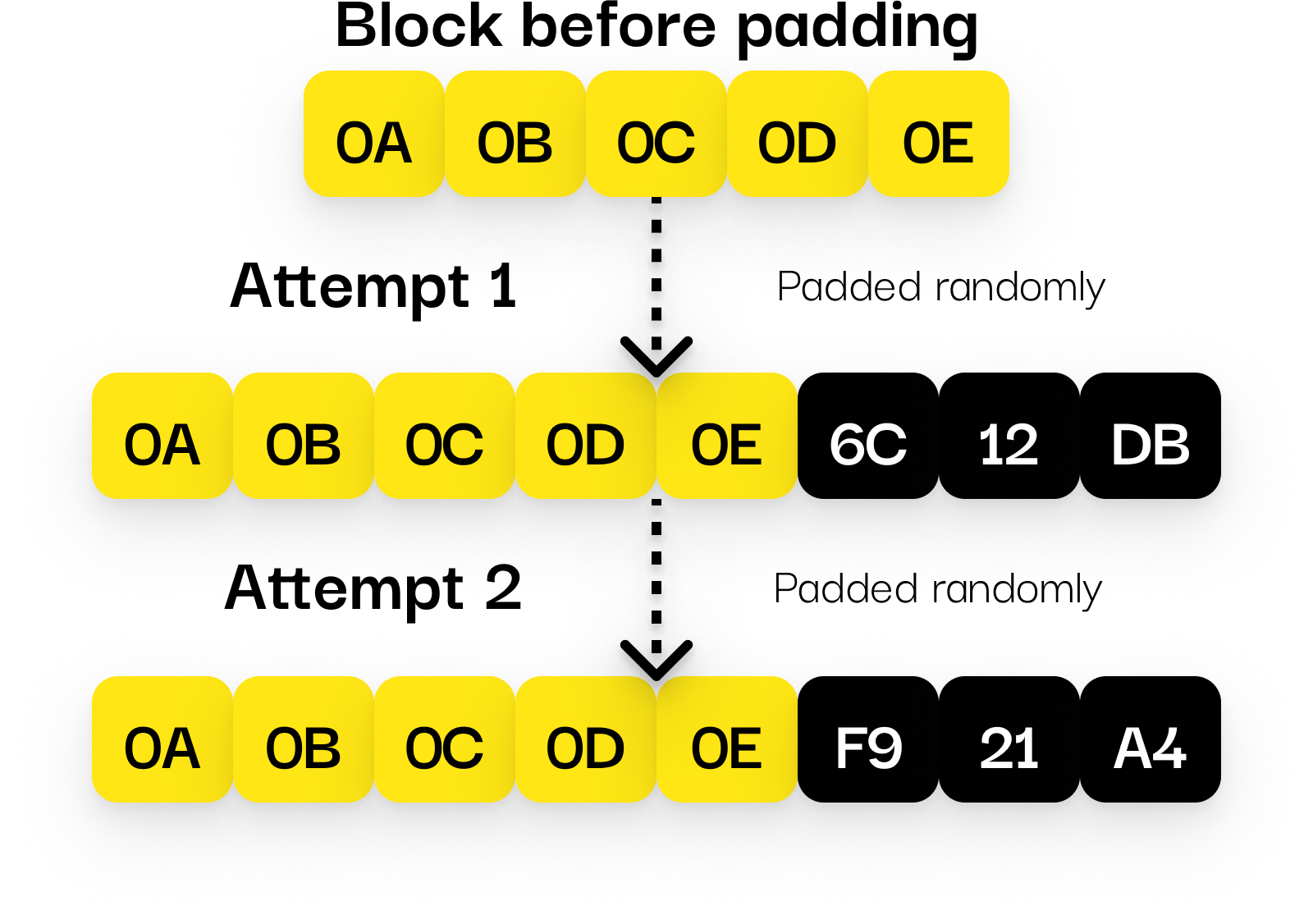
XTEA256 (like most block ciphers) encrypts data in 8-byte blocks.
If your message is not a multiple of 8 bytes, it needs to be padded.
🧪 How It Works
Instead of adding fixed padding bytes, random values are added to fill the last block.
- The length of the actual message is stored separately
- Padding is stripped after decryption
- Each encryption attempt generates a different encrypted result, even for identical messages
🛡️ How Padding Prevents Key Recovery
Without random padding, encrypted packets would always end in predictable bytes
(like multiple 0x00 values). This can leak information when decrypting with the wrong key.
For example:
- If your message is 1 byte, the last 7 bytes will be padding
- Without randomness, these 7 bytes would always be the same (e.g.
0x00) - An attacker could try random keys and check if the decrypted padding looks "valid"
This would make it easier to guess or brute-force the session key over time.
By using random padding:
- Each decryption attempt produces unpredictable results
- There's no way to verify if a wrong key was "almost correct"
- The padding cannot be guessed, making key recovery practically impossible
🧠 Benefits
- ❌ Prevents detecting repeated messages
- 🔐 Makes it impossible to compare encrypted payloads
- 🔄 Protects against pattern analysis
- 🧩 Ensures that each packet appears unique, even if message is the same
Randomized padding is automatically handled by the library.
You don’t need to manually add or remove it.